Houston faces significant environmental challenges, from frequent flooding to the long-term impacts of climate change. As one of the fastest-growing cities in the United States, Houston must balance economic growth with sustainability. Through innovative flood management, infrastructure development, and environmental initiatives, the city is working to build resilience for the future.
Flooding: A Persistent Threat
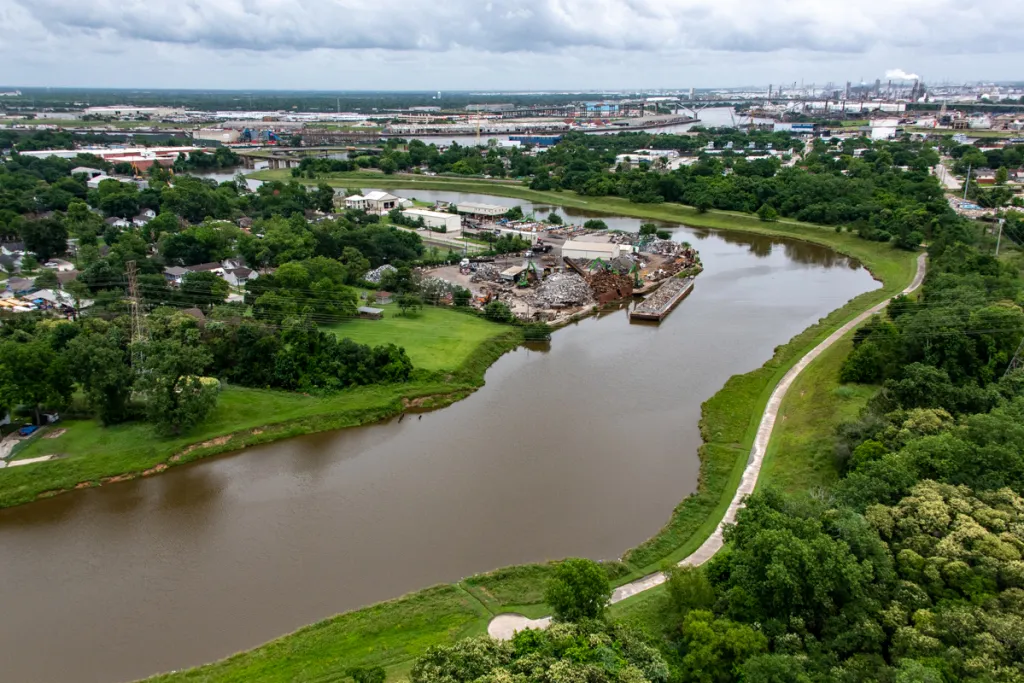
Houston’s flat topography and proximity to the Gulf of Mexico make it highly prone to flooding. The city’s network of bayous – designed to manage water – often struggles to handle the volume of rainfall during intense storms. In recent years, hurricanes and tropical storms have exacerbated the problem, leading to devastating floods.
The 2017 Hurricane Harvey was a stark reminder of the city’s vulnerability. The storm dumped more than 50 inches of rain over several days, causing widespread damage and displacing thousands of residents. Floodwaters inundated homes, businesses, and public infrastructure, prompting a re-evaluation of Houston’s flood management strategies.

Infrastructure Improvements and Flood Mitigation
In response to the increasing frequency of flooding, Houston has invested in major infrastructure improvements. The city has expanded drainage systems, deepened bayous, and constructed detention basins to manage stormwater more effectively.
Buffalo Bayou Park is one example of a dual-purpose infrastructure project. The park serves as both a recreational area and a flood detention basin, capturing excess water during heavy rains. Additionally, Houston is working with the Harris County Flood Control District to improve levees, reservoirs, and stormwater management systems.
Another key initiative is the Project Brays flood control project, which involves widening sections of Brays Bayou and improving bridges to reduce flood risks. These efforts demonstrate Houston’s commitment to building resilience in the face of future storms.

Climate Change: A Growing Challenge
Houston’s geographical location makes it particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Rising sea levels, warmer temperatures, and more frequent extreme weather events pose ongoing challenges. The city also experiences urban heat island effects, where densely built areas retain more heat, worsening air quality and increasing energy consumption.
To combat these challenges, Houston has launched the Climate Action Plan, which aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainability. The plan focuses on renewable energy, public transit expansion, and energy efficiency improvements. Houston is also encouraging green infrastructure, such as living roofs and permeable surfaces, to help mitigate the effects of urbanization.

Community Engagement and Environmental Justice
Houston’s environmental policies emphasize the importance of community involvement. The city actively collaborates with residents, nonprofit organizations, and businesses to promote sustainable practices. Educational programs raise awareness about flood preparedness, waste management, and energy conservation.
Additionally, Houston is committed to environmental justice, ensuring that underserved communities, which are often disproportionately affected by flooding and pollution, have access to resources and support. Initiatives such as tree planting campaigns and clean air projects aim to improve the quality of life for all residents.
Building a Sustainable Future
Looking ahead, Houston’s leaders are working to create a sustainable, resilient city. The focus on green infrastructure, renewable energy, and climate adaptation reflects a commitment to long-term environmental health. Projects like the Houston Green Corridor are transforming urban spaces into eco-friendly areas that support both biodiversity and recreation.
Houston’s response to environmental challenges showcases its ability to adapt and innovate. While the city’s geography and climate present obstacles, proactive planning and community engagement are helping to build a brighter, more sustainable future.